Catalase Test- Principle, Procedure, and Result Interpretation.
Join our learning channel to get more lessons for free labQMS
Join our learning channel to get more lessons for free labQMS
CATALASE TEST-PRINCIPLE,PROCEDURE AND RESULT INTERPRETATION
Catalase is an enzyme produced by microorganisms that live in oxygenated environments to neutralize the bactericidal effects of toxic forms of oxygen metabolites such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The catalase enzyme protects aerobes and facultative anaerobes from oxidative damage. Anaerobes generally lack the catalase enzyme. Catalase is also a significant staphylococcal virulence factor.Normally 3% Hydrogen perioxide is used in routine culture while 15% Hydrogen perioxide is used for detection of catalase in anaerobes.
Table of Contents
1.0 Purpose
2.0 Scopes
3.0 Principle
3.1 Superoxol test
4.0 Materials
5.0 Specimen
6.0 Quality Control(QC)
7.0 Procedures
8.0 Interpretation
9.0 Reporting
10. Precaution
11.References and further reading
1.0 Purpose
The purpose of this procedure is to provide instructions on how to perform Catalase Test in identification of Gram Positive bacterial.
2.0 Scope
This procedure will be used for providing instruction on how to perform Catalase Test
3.0 Principle
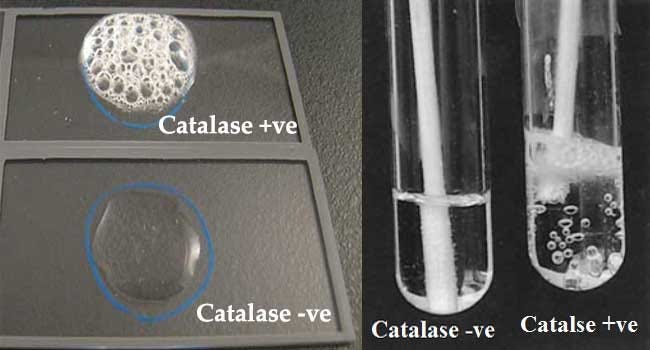
Bacterial that synthesize the enzyme Catalase will hydrolyze Hydrogen perioxide into water and gaseous oxygen,which result into liberation of gas bubbles.
Catalase Test separate staphylococcus (Positive) from streptococcus and Enterococcus(Negative) ,gram positive Rods like sporeforming bacterial can also be differentiated using catalase test,Where Bacillus species are Catalase Positive and Clostridium species are Catalase Negative,percentage of hydrogen perioxide used for these anaerobic bacterial is around 15% compaired to 3% used in routine culture.
Catalase Test can also used in differentiating Neisseria species using Superoxol test,this is simple test which utilize 30% of hydrogen perioxide as reagent.Neisseria gonorrhoeae produces an enhanced elaboration of bubbles which is not seen in other members of the genus due to superoxol.
3.1 What is superoxol test
Superoxol test-Is a catalse test that uses 30% hydrogen perioxide as a reagent.Was used to differentiate neisseria gonorrhoeae from other neisseria species,a positive test was define as immediate brisk bubbling up when 30% hydrogen perioxide was dropped on bacterial colony.99.9% of gonococci are superoxol positive ,only 1% of neisseia species isolated from Modified Thayer Martin Agar was Superoxol Negative .
4.0 Materials
Catalase Reagent:3% Hydrogen perioxide-Dilute 30% Hydrogen perioxide 1:10 in deonized water and store at 2–8 oC
Superoxol reagents for Neisseria :30%Hydrogen perioxide stored at 2–8oC
Glass slide
sterile wooden sticks/Inoculating loop
NB:Reagent may be stored up to six months
5.0 Specimen
Young culture incubated from18–24 hours,prefered from Blood agar plate or chocolate agar
6.0 Quality Control
We have positive control which is control organism -Staphylococcus aureus-ATCC-33592
Negative control -Enterococcus faecalis-ATCC-29212
7.0 Procedure
Touch the center of a well -isolated colony with loop/stick then transfer to a clean glass slide , be sure colony is visible to the naked eye on slide,if colony is blood Blood agar be carefull not to pick Red blood cells.
Place one drop of hydrogen perioxide reagent on slide and observe immediately for bubbles appearance.Do not mix reagents and colony,use magnifying lense to observe for bubles if necessary.
Discard the slide into sharps container
8.0 Interpretation
Positive:Immediately appearance of bubbles-Staphylococcus species
Negative:Shows no bubbles-Streptococcus species
9.0 Reporting
For Neisseria spp:Record as Superoxol positive or superoxol negative
For other bacterial:Record as Catalase positive/Catalase test negative
10.0 Precautions
Be careful while taking colony from Blood agar Not to pick Red blood cells ,this will cause false positive since red blood cells contains catalase
30% hydrogen perioxide is extremely caustic to skin.if contact occurs wash immediately with 70% ethly alcohol not water
Do not pick colonies that are older than 24hrs because enzyme is present in viable culture only.older culture may give false negative result
11.0 References and further readings
Tille, P. (2017). Bailey & Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology (14 edition). Mosby.
Procop, G. W., & Koneman, E. W. (2016). Koneman’s Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology (Seventh, International edition). Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.
Karen Reiner. (2010). Catalase test protocol. American Society for Microbiology
Clinical Microbiology Procedures Handbook, Fourth Edition. (2016). American Society for Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1128/9781555818814
Mandell GL. Catalase, superoxide dismutase, and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. In vitro and in vivo studies with emphasis on staphylococcal–leukocyte interaction. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):561–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI107963. PMID: 1117067; PMCID: PMC301784.
Similar Post
identification of gram-positive bacterial flow chart
Join our news letter for more updates daily